Xuesong Wu

Xuesong Wu, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, PR China
Short biography : Xuesong Wu is currently a professor at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his PhD in organic chemistry from the University of Science and Technology of China in 2012 under the supervision of Professor Shi-Kai Tian. From 2012 to 2017, he did postdoctoral research with Professor Haibo Ge at IUPUI and Professor Vy M. Dong at UC Irvine. In 2018, he joined the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Huazhong University of Science and Technology as a group leader. His current research interests focus on the development of efficient and practical methods for organic synthesis, involving organic radical chemistry, photochemical synthesis, and asymmetric catalysis.
Light-Driven Multicomponent Radical Reactions with Sulfur-Containing Small Molecules
Xuesong Wu (吴雪松)
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
e-mail: xswu@hust.edu.cn
Keywords:radicaldeoxygenation, thiocarbamoylation, energy transfer, hydrogen atom transfer
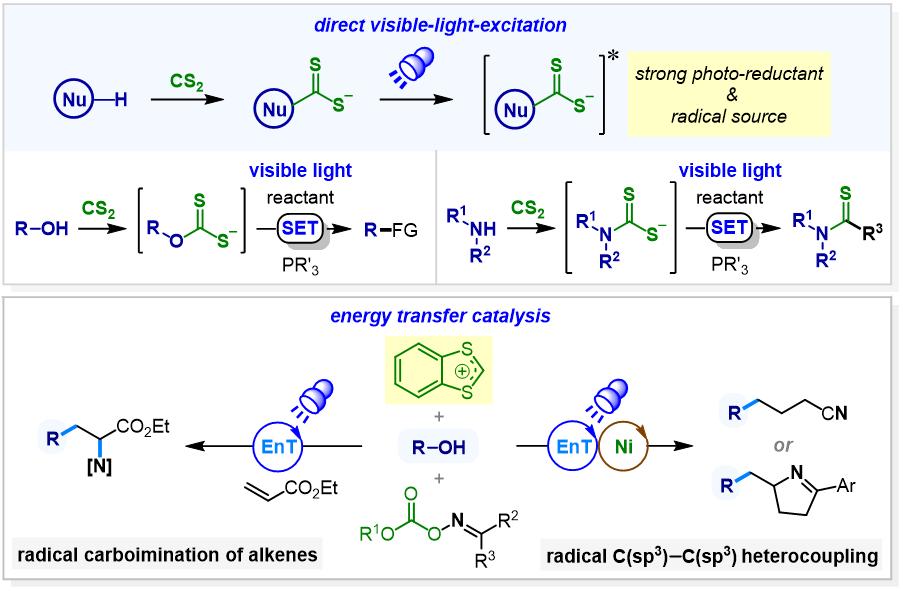
Sulfur-containing organic structures frequently exhibit low redox potentials, low bond energies, and the capacity to stabilize adjacent carbocations and radicals. These characteristics contribute to the high reactivity of sulfur-containing groups and motifs. We have developed a strategy that utilizes sulfur-containing small molecules to convert relatively inert organic molecules into more reactive substances to participate in single electron transfer or hydrogen atom transfer processes. This strategy has been demonstrated to facilitate a series of novel light-driven multicomponent radical reactions, including: 1) Visible-light-promoted deoxygenative radical transformations of diverse primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols[1] that were enabled by inexpensive carbon disulfide- and phosphine-assisted C–O bond activation via xanthate salt intermediates.[2] 2) Visible-light-driven multicomponent radical reactions of amines, carbon disulfide, and olefins in the presence of phosphines for mild, efficient, and versatile synthesis of acyclic thioamides, as well as γ-thiolactams.[3] 3) Photocatalytic energy transfer (EnT)-driven deoxygenative radical coupling reactions of alcohols with bifunctional oxime carbonates enabled by applying the 1,3-benzodithiolylium (BDT) cation as an efficient hydroxyl-activating reagent.[4]
References
[1] Y.-X. Wu, M.-R. Chang, Z.-P. Guan, R. Chi, J.-X. Yu, X. Wu, and Z.-B. Dong, Sci. China Chem.,2025, 68, 4595–4641.
[2] H.-M.Guo, and X. Wu, Nat. Commun.,2021, 12, 5365..
[3] H.-M.Guo, J.-J.Wang, Y. Xiong, and X. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2024, 63, e202409605.
[4] B.-Q.He, L. Zhao, J. Zhang, W.-H. Bao, M. Yang, and X. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2025, 64, e202423795.
Acknowledgement:We gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22271109) for financial support.
